1. Introduction
Many innovations have been developed to improve vannamei shrimp cultures. Probiotics, for example, are non-pathogenic bacteria that live in the host intestine and provide positive health effects by improving the host’s immune system to fight disease and aiding in host development . These beneficial bacteria have been widely used in the shrimp industry and are often supplemented through food and injection. Meta-analysis data from 100 studies have shown that probiotics can increase the survival rate of vannamei shrimp by up to 95% compared to controls. In vannamei shrimp, probiotics strengthen the immune system against pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and environmental factors.
2. Probiotic Mechanisms to Improve Vannamei Shrimp Aquaculture Performance
Bacteria like Bacillus, Lactobacillus, Enterococcus, Alteromonas, and Arthrobacter spp. can enhance shrimp aquaculture performance through various mechanisms, including gut colonization, antagonistic activities, digestive enzyme secretion, organic waste removal, and supplemental nutrient production. Bacteria enter the intestine, restoring the gut microbiome and introducing beneficial functions. Symbiotic relationships in the intestines can include mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Probiotics function to colonize the gut in beneficial ways.
Probiotics activate insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) by increasing short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), which binds to receptors on the cell surface and activates cell proliferation and differentiation. These fatty acids also perform antagonistic activities, producing metabolites that trigger gene expression changes. Probiotics deactivate histone deacetylase and elevate GH through gene expression.
Probiotics also help break down nutrients into simpler forms, increasing digestive enzyme secretion and producing nutrients for the host body. They also play an external role in water quality, reducing the amount of organic material in water, which can turn into ammonia, a toxic compound. Probiotics also increase dissolved oxygen content in water, facilitating photosynthesis.
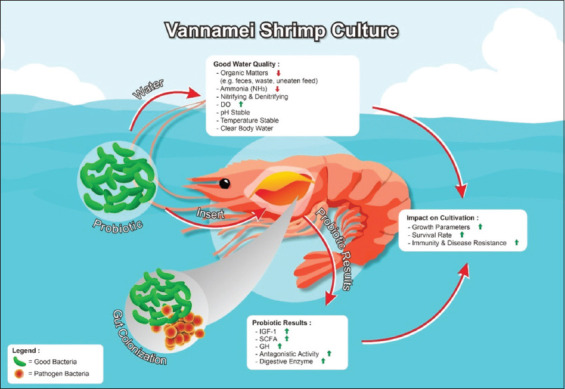
Figure 1. Role of probiotics in vannamei shrimp aquaculture
3. Field Applications
Probiotics are administered to various types of shrimp, including water, immersion, oral, and injection. Water-added probiotics absorb nutrients, starving pathogenic bacteria. Oral probiotics increase gut microflora and improve growth during feeding. Microencapsulation improves water quality and health, but requires continuous check of viability. Direct injections ensure probiotics enter the body, but time and cost are disadvantages. These methods can be used to improve shrimp health, but their specific target remains unspecified.
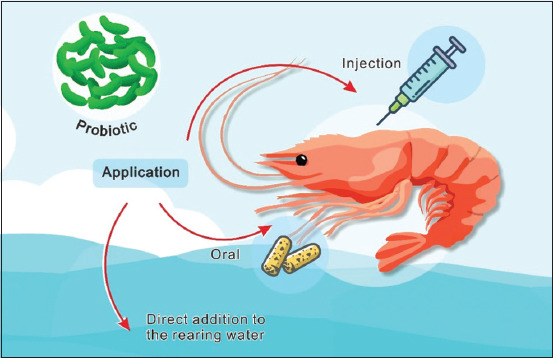
Figure 2: Administration way to deliver probiotics to vannamei shrimp
4. Conclusion and Future Outlook
Shrimp aquaculture diseases are primarily caused by pathogenic bacteria and viruses, leading to resistance to antibiotics. Probiotics, as dietary supplements, can help eliminate pathogens and improve shrimp's immune health without affecting their health. However, improper application can lead to excessive nutrient production and microbial disturbances. Further research is needed to understand the genetic makeup and transcriptomic profiles of probiotics, as well as other natural alternatives like paraprobiotics, algae, and plant extracts. Probiotics have shown higher effectiveness in increasing shrimp yield compared to antibiotics.
References: Muhammad Kholiqul Amiin, Almira Fardani Lahay, Rizha Bery Putriani, Muhammad Reza, Septi Malidda Eka Putri, Md Afsar Ahmed Sumon , Mamdoh T Jamal, Muhammad Browijoyo Santanumurti - National Library of Medicine

 Facebook
Facebook  Youtube
Youtube  VN
VN

 Youtube
Youtube  Linkedin
Linkedin  Facebook
Facebook 
